Judicial Protection of Intellectual Property Rights by Shanghai Courts in 2021
In 2021, Shanghai courts fulfilled their functions of offering judicial protection of intellectual property rights (IPRs), strengthened judicial protection of IPRs, and further promoted the implementation of fair competition policies. By continuously improving the trial mechanisms, Shanghai courts heard various types of intellectual property (IP) cases in a fair and efficient manner in order to provide high-quality and efficient IP-related judicial services and guarantee for developing Shanghai into a highland in IPR protection, creating a law-based business environment, and sustaining healthy economic development.
I. General Situation of IP Case Trials
(1) The total number of IP cases continued to increase. In 2021, Shanghai courts accepted a total of 53,279 IP cases and concluded 49,100 cases, up 32.49% and 30.88% respectively from last year. The number of accepted cases saw a substantial growth (Figure 1).
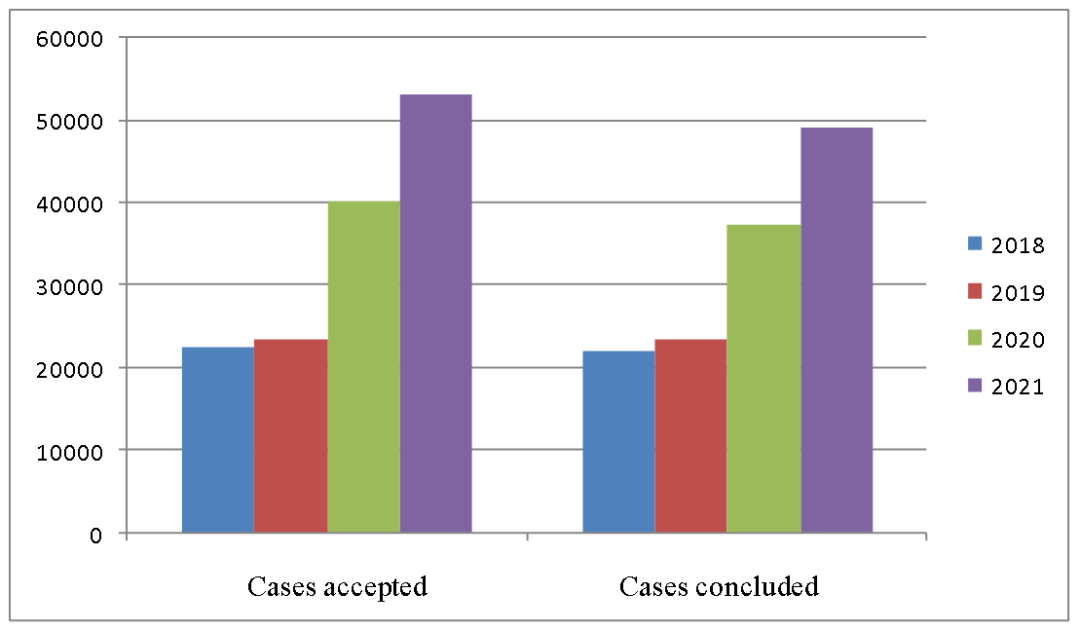
Figure 1: Comparison of IP Cases Accepted and Concluded by Shanghai Courts in 2018-2021
A total of 52,110 cases accepted and 48,106 IP cases concluded were first-instance IP cases, representing a year-over-year growth of 32.39% and 31.11% respectively. Among them, 51,122 cases accepted and 47,035 cases concluded were civil IP cases, up 31.83% and 29.92% respectively from last year (Figure 2); 979 IP cases accepted and 1,064 IP cases concluded were criminal cases, up 51.55% and 93.10%; and 9 cases accepted were administrative IP cases, up 6 from last year, and 7 administrative IP cases were concluded, basically remaining unchanged compared to last year. The numbers of cases of first instance concerning trademark disputes, patent disputes and unfair competition disputes increased significantly, whilst the growth of the number of cases related to copyright disputes and franchise contracts slowed down (Figure 3). The number of cases involving large amount of claims continued to see a significant increase (Figure 4).
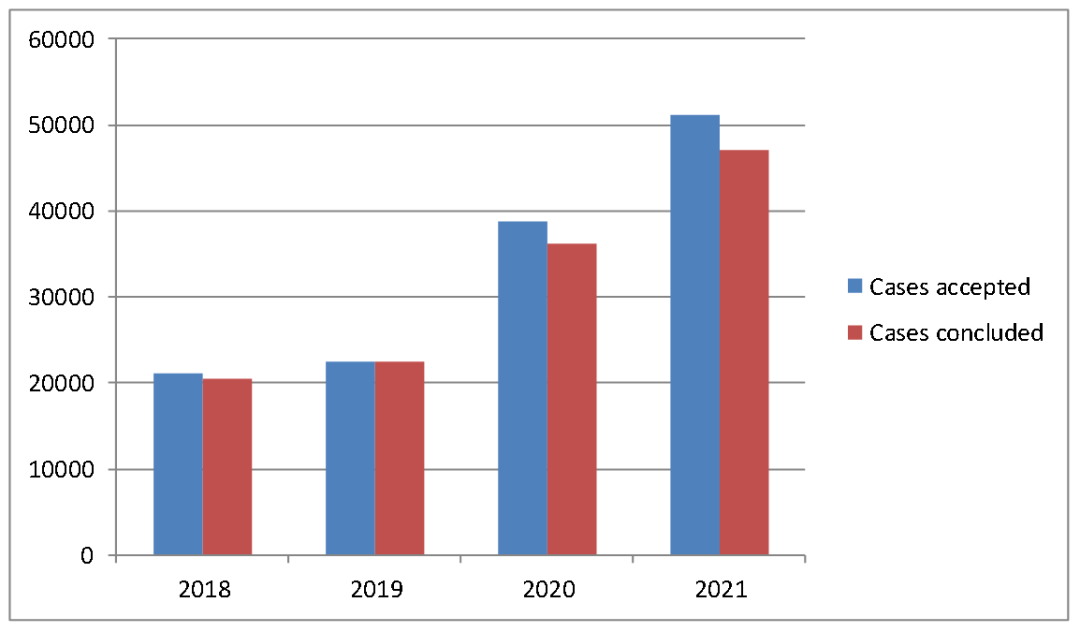
Figure 2: Trend Chart of Accepted and Concluded First-Instance Civil IP Cases of Shanghai Courts in 2018-2021
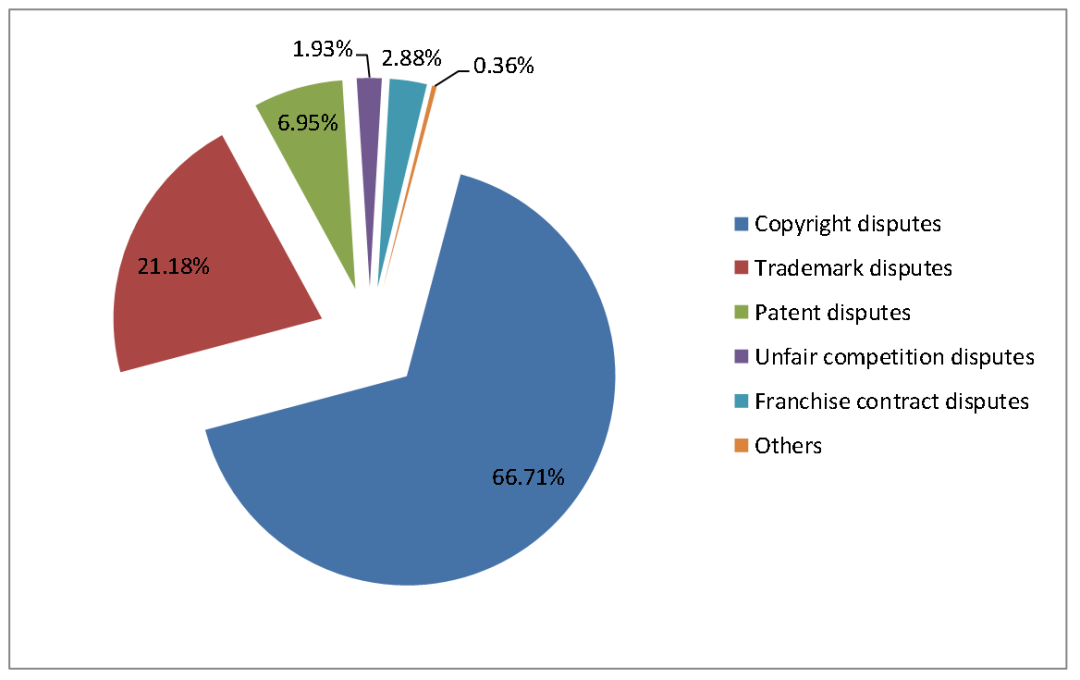
Figure 3: Types of First-Instance Civil IP Cases Accepted by Shanghai Courts in 2021
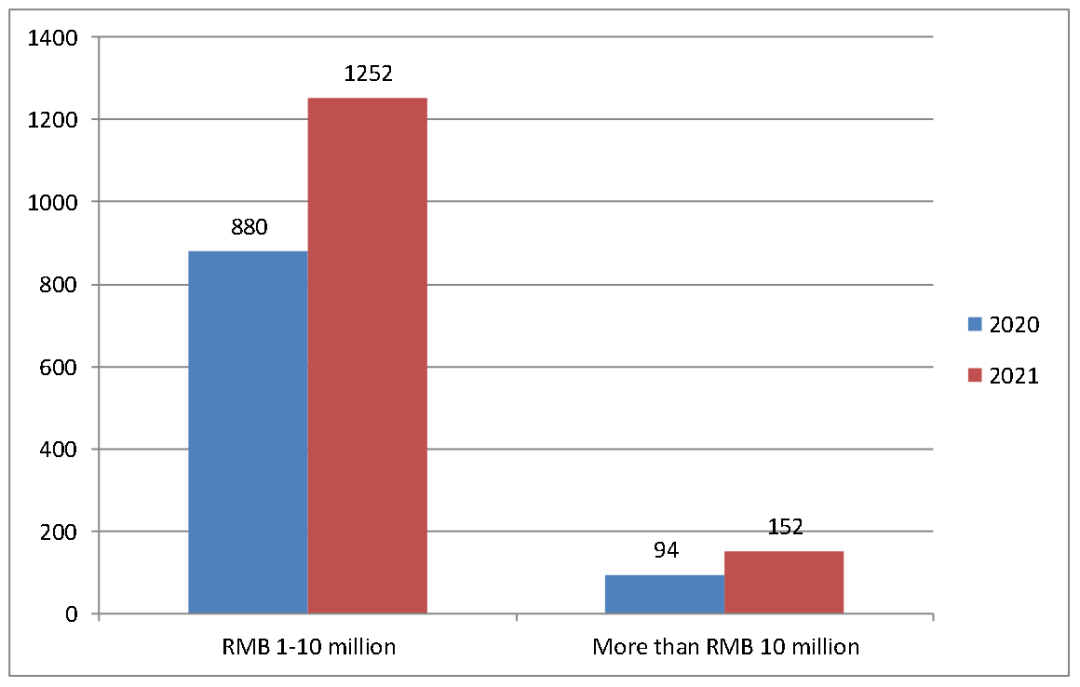
Figure 4: Comparison Chart of Amount of Claims of Civil IP Cases Accepted by Shanghai Courts in 2020 and 2021
(2) The trial effectiveness and efficiency improved steadily. Facing new issues and situations including the substantial increase in cases accepted and COVID-19 prevention and control, Shanghai courts managed to overcome difficulties, strived to complete various judicial tasks and achieved fairly good trial quality and efficiency. In 96.93% of first-instance cases, litigants were willing to accept the judgments rendered; the ratio of cases concluded within the time limit for case handling reached 99.59%, basically remaining unchanged compared to last year.
(3) Model cases achieved fruitful results. Shanghai Yinneng Industrial Co., Ltd. v. Ninghai Zhesheng Plastics Factory over invention patent infringement dispute, with Shanghai Intellectual Property Court as the court of first instance and the High People’s Court of Shanghai Municipality (Shanghai High People’s Court) as the court of second instance, was selected into the Gazette of the Supreme People’s Court in 2021. The case of copyright infringement crime filed against Liang Yongping, Wang Zhenghang and other 13 defendants, which was tried by the Third Intermediate People’s Court of Shanghai Municipality and Yangpu Primary People’s Court, was selected as one of “2021 Top 10 IP Cases of Chinese Courts”. The case of Shanghai Erguang Catering Management Co., Ltd. v. Shanghai Zaigao Catering Management Co., Ltd. over the counterfeiting, false advertising and commercial defamation dispute was selected as one of “2021 Top 50 Typical IP Cases of Chinese Courts”. “Lufax financial service platform” (case of an unfair competition dispute), heard by Pudong New Area Primary People’s Court, was selected into the “10 Model Anti-monopoly and Anti-unfair Competition Cases of the People’s Courts”. In addition, 2 judgments of IP cases released by Shanghai courts were selected for the 4th “Top 100 Judgments of Chinese Courts”, and 1 IP case was selected into the “Top 100 Hearings of Chinese Courts” within national courts. In the Selection of 2021 Excellent Case Analysis of Chinese courts, 3 IP cases analyses submitted by Shanghai courts won the second prizes, along with 1 third prize and 1 honorable mention.
(4) Cases with social influence kept increasing. A number of IP cases tried by Shanghai courts have attracted the attention from relevant sectors and the society. For example, Jin Xin v. Apple Inc et al. over monopoly dispute involved the determination of whether the defendant has abused its dominant market position to commit tying and charge unfairly high prices. Tesla (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. v. Zhongyin Food Co., Ltd. et al. over the trademark infringement and unfair competition dispute involved the determination of the well-known trademark “Tesla”. China UnionPay v. Shandong Shengyun Information Co., Ltd. over trademark infringement dispute involved the determination of well-known trademarks “QuickPass” and “Cloud QuickPass”. Nongfu Spring Co., Ltd. v. Zhongxian Menghong Agriculture Co., Ltd. et al. over unfair competition dispute involved the determination of the well-known product name “17.5 °” that has certain influence. Shanghai CanXing Culture & Media Co., Ltd. v. Hubei Shijue Yinxiang Culture & Media Co., Ltd. over unfair competition dispute involved the famous variety show “The Voice of China”, etc.
(5) Difficult and complicated cases and new types of cases caused concerns. In the case of Guangzhou Deli Yacht Marina Engineering Co., Ltd. v. Nanchong City Landscape Management Office and China Construction Third Engineering Bureau Co., Ltd. et al. over design patent infringement dispute, the court legally protected the reasonable reliance interest of the parties through the determination of “patent implied license”. In the case of Fendi Co., Ltd. v. Shanghai Yilang International Trade Co., Ltd. and Pioneer Capital Outlets (Kunshan) Commercial Development Co., Ltd. over trademark infringement and unfair competition dispute, the court clarified the identification rules for the reasonable use of the trademark. Three cases were involved in emerging issues like the determination of design patent infringement of mobile phone graphical user interface. These cases included: the case of Suzhou Dajiaying Information Technology Co., Ltd. v. Shanghai Zecao Network Technology Co., Ltd. over design patent infringement dispute; the case of Beijing Jinshan Security Software Co., Ltd. v. Shanghai Mengjia Network Technology Co., Ltd. over design patent infringement dispute; and the case of Beijing Jinshan Security Software Co., Ltd. v. Shanghai Chubao Information Technology Co., Ltd. and Shanghai Chule (Coo Tek) Information Technology Co., Ltd. over design patent infringement dispute.
II. Political loyalty consolidated through education and rectification within the team
(1) Party history learning and education activities were carried out to improve political integrity. The IP Division of Shanghai High People’s Court formulated the Party History Learning and Education Plan of the Party Branch of the IP Division and launched a number of such activities, including the Bus Classroom of “One-hundred-Year Party History, A New Journey of Endeavor”, the activity of “Recalling the History of the Court, Learning the Party History and Remaining True to Our Original Aspiration”, and “Reading · Knowing · Doing” Party history books recommending and sharing sessions, to create a sound atmosphere of learning and ensure the effectiveness of Party history learning. The First IP Division of Shanghai IP Court held a special organizational life meeting focusing on “Learning the Party history, Understanding its theories, Doing practical work and making new advances” to motivate their daily work. The IP Division of Xuhui Primary People’s Court carried out Party Day activities of “immersive” Party history learning and education, calling upon all of the judges, court staff, and judicial personnel to stay true to their original aspiration and to serve the people.
(2) Education and rectification within the team was carried out to ensure tangible results. The IP Division of Shanghai High People’s Court held an opinion-collecting session on team education and rectification, listened to and valued inputs of IP-related functional departments as well as the intermediate and primary courts; carefully implemented greater accountability for improving Party conduct, and carried out warning education on “not daring to, being unable to and having no desire to commit acts of corruption”. The IP Division of Shanghai High People’s Court also learnt from heroes and role models to carry forward uprightness, and strived to practice “Serving the People Heart and Soul and Being Grateful for the Kindness” to fulfill the motto that “Belief in Hearts, Strength in Acts”. The IP Division of Pudong New Area Primary People’s Court utilized the “Three Meetings and One Lesson” and thematic Party Day activities to carry out the study of Xi Jinping Thought on the Rule of Law, Party rules and disciplines, as well as campaigns of learning from heroes and role models. The IP Division of the Primary People’s Court of Yangpu District combined education and rectification with the promotion of the “Four Dares” (dare to innovate, dare to contend for first place, dare to tackle toughest challenges, and dare to take up the responsibility) guideline to encourage Party members to play an exemplary role in making achievements in their posts. The IP Division of Putuo Primary People’s Court organized various efforts to thoroughly expose and rectify deep-rooted problems in six major aspects and other prominent problems and took a series of measures including policy publicity, self-inspection and self-correction, clue verification, key case evaluation and intelligent data investigation to go deep into the problems and promote the work of “Investigation, Rectification, Improvement and Establishment” in an all-round way.
(3) The “I Do Practical Things for the People” series of activities were put into practice to respond to new demands for IP protection. The IP Division of Shanghai High People’s Court took the lead in implementing the key program of “I Do Practical Things for the People” among Shanghai courts, “Continuously improving the efficiency and effectiveness of judicial protection of IPRs”. The IP Division of Shanghai High People’s Court visited e-commerce platforms to actively respond to their demands; and carried out investigation on the pains and difficulties in the collective management of musical works to improve relevant judicial rules. The Second IP Division of Shanghai IP Court efficiently and legally conducted preservation of evidence, and completed the preservation work at the exhibition site according to the original plan despite the landing of severe Typhoon In-Fa in Shanghai. The IP Division of Xuhui Primary People’s Court joined hand with deputies of District People’s Congress and members of the District CPPCC Committee to launch the visiting event “Satisfaction in Xuhui, Serving in Local community”, communicated and coordinated with the residents about the problems encountered during the building of Civilized Districts as well as in the epidemic prevention and control.
III. Remarkable success in IPR protection enabled by fair and efficient judicature
(1) Punitive damages were applied in accordance with the law to increase compensation for damages. Danisco v. Yueyang Ruikang Biotechnology Co., Ltd. et al. over invention patent infringement dispute was the first case handled by Shanghai courts to apply punitive damages for patent infringement, in which the defendants were ruled to pay the damages of RMB 11 million based on evidences. In the case of Huayi Brothers Media Corporation v. Pingshan District Times Huayi Studios et al. over trademark infringement and unfair competition dispute, the court determined that the royalty of the trademark involved in the case was RMB 300,000 based on evidences, and thus determined three times punitive damages based on the infringement behavior and subjective intent. In the case of Unilever China Investment Co. Ltd. v. Wang Fulong, Xu Shupin et al. over trademark infringement dispute, the claim of the plaintiff for a compensation of RMB 700,000 was supported in full amount through the application of punitive damages.
(2) A law-based business environment was created to provide equal protection of IPRs. Shanghai courts provided equal protection of the legitimate rights for both domestic and overseas parties and cracked down on various IP infringement acts. In the case of Siemens AG v. Xiaomi Communications Co., Ltd. over invention patent dispute, the court identified the royalty of standard essential patents (SEPs) involved in the case through a “top-down approach” and the defendant was ruled to compensate over RMB 12 million. In the cases of Casio Computer Co., Ltd. v. Shanghai Xuanfeng Trade Co., Ltd. et al. over a series of disputes on design patent, which involved the industrial design of famous product “Casio Watches”, a total of RMB 8.8 million was awarded collectively in the three cases based on the sales data from relevant e-commerce platforms. In the case of Entertainment One UK Ltd. v. Chen Jianguang and Shanghai Xunmeng Information Technology Co., Ltd. over trademark infringement dispute, “Peppa Pig” was declared a well-known trademark by the court in accordance with the law and the defendants were ruled to compensate for the losses of the plaintiff. After the case was concluded, the court received a letter of thanks from the British Consulate-General Shanghai expressing that the trial of this case greatly protected the legitimate rights and interests of foreign-invested enterprises operating in China.
(3) Crackdown on crimes was intensified to continuously improve the market environment. Shanghai courts intensified punishment for IPR infringement and concluded a number of major criminal IP cases. In the series of cases involving crime of counterfeiting the registered trademarks of Chanel, Gucci and other luxury clothing, amount involved exceeded RMB 43 million, and the 50 defendants were sentenced to fixed-term imprisonment of different periods ranging from five years and nine months to one year and three months in addition to total fines of RMB 22 million. In the series of cases involving crime of counterfeiting the registered trademark of Cartier, the amount involved exceeded RMB 61 million, and the 21 defendants were sentenced to fixed-term imprisonment of different periods ranging from five years and nine months to eight months in addition to fines. Besides, Shanghai courts concluded a batch of criminal IP cases with high public concern and great influence, such as the copyright infringement case of YYeTs and the case of defendant Liu (X) yang illegally manufacturing the registered trademark of “Ferrero in Chinese”.
IV. Judicial functions fulfilled to serve the overall situation and empower active actions
(1) Services were provided to ensure high-level reform and opening-up of Pudong New Area. Shanghai High People’s Court and Pudong New Area Primary People’s Court actively participated in the argumentation of Several Regulations of Shanghai Pudong New Area on Establishing a High-Level Intellectual Property Protection System to provide legislative guarantee for Pudong’s high-level reform and opening-up. More specifically, Shanghai High People’s Court held a session in Pudong New Area Primary People’s Court on the building of a leading area for judicial services and guarantee of intellectual property rights, further implemented the guiding principles in documents released by the CPC Central Committee and the central government and supported Pudong New Area Primary People’s Court to play a leading and exploratory role. Under the guidance of Shanghai High People’s Court, Pudong New Area Primary People’s Court released the Ten Measures by Shanghai Pudong New Area Primary People’s Court for Building a Leading Area for Judicial Protection of Intellectual Property Rights and Serving the High-level Reform and Opening-up of Pudong New Area, thus providing strong judicial services and guarantee for the building of the leading area.
(2) The judicial guarantee mechanism was enhanced to provide judicial guarantee for China International Import Expo (CIIE) and China Flower Expo. The IP Division of Shanghai High People’s Court and Putuo Primary People’s Court held the First CIIE-related IP Protection Forum and a series of investigations and symposia to actively listen and respond to the demands for CIIE-related IP protection. The IP Division of Shanghai High People’s Court and Yangpu Primary People’s Court carried out in-depth investigation at the headquarters of China Flower Expo and held a meeting to exchange ideas with personnel in charge of the headquarters and Chongming District Administration for Market Regulation. Yangpu Primary People’s Court formulated the Guideline on Providing Intellectual Property Judicial Service Guarantee for the 10th China Flower Expo and put forward 14 concrete measures. The court also established an IP circuit trial station in the Garden during the Flower Expo, and adopted the way of online case filing and on-the-spot hearing to handle the geographical indication (GI) certification trademark infringement case of “Chongming Rice” sold in the exclusive shop in the Garden, after which it received a letter of thanks from the Executive Committee of the Flower Expo.
(3) Judicial publicity activities were carried out to improve the law-based business environment. During the 21st World Intellectual Property Day, Shanghai High People’s Court and Shanghai IP Court jointly held a press conference and issued several documents both in Chinese and English, including the White Paper of Intellectual Property Protection by Shanghai Courts in 2020 and Judicial Protection of Intellectual Property Rights by Shanghai Intellectual Property Court in 2020, as well as “Top Ten Cases on Judicial Protection of Intellectual Property Rights by Shanghai Courts in 2020” and “Typical cases on Strengthening Protection of Intellectual Property Rights by Shanghai Courts in 2020”, and officially launched the IP case management system of Shanghai courts. Shanghai IP Court held a press conference to issue a white paper on trial of cases involving unfair competition from 2015 to 2020 along with typical cases. Pudong New Area Primary People’s Court held a press conference to release a white paper on providing judicial services and guarantee for building a business environment favorable to foreign-related IP protection and ten measures to comprehensively strengthen judicial services and guarantee for foreign-related IP protection along with typical cases. Yangpu Primary People’s Court issued a white paper on trial of criminal copyright cases along with typical cases. Xuhui Primary People’s Court visited Shanghai Xunmeng Information Technology Co., Ltd., an e-commerce enterprise, to offer judicial suggestions to prevent and resolve disputes from the litigation source and strengthen IP protection in the e-commerce field.
V. Continuous innovation efforts made to further optimize IP trial mechanism
(1) The “Three-in-One” trial mechanism was improved to enhance coordinated protection. The IP Division of Shanghai High People’s Court joined hands with the Fourth Procuratorial Department of Shanghai People’s Procuratorate and the Food, Drug and Environment Crime Investigation Detachment (FDECID) of Shanghai Municipal Public Security Bureau to formulate the Interim Measures on the Transfer and synchronous Investigation of Criminal Clues in Civil and Administrative Proceedings of Intellectual Property Rights, giving full play to the functions of the “Three-in-One” trial mechanism and strengthening coordination among public security authorities, procuratorial authorities and people’s courts, thus forming a synergy of IP protection in civil, administrative and criminal proceedings. Yangpu Primary People’s Court and Xuhui Primary People’s Court respectively signed cooperation agreements with procuratorates, public security bureaus and administrations for market regulation of their own district to intensify coordinated IP protection in criminal and administrative proceedings, ensure seamless connection between administrative enforcement and criminal justice and facilitate all-round protection of IPRs. Yangpu Primary People’s Court signed the Opinions on Standardizing the Transfer of Suspected Criminal Clues and Cooperation Through Team Work with the district’s public security bureau and procuratorate and established a joint conference system to ensure efficient transfer of criminal clues and form a synergy to crack down on criminal IP offences.
(2) Efforts were made to push the reform of improving the trial levels and functional orientations of courts structured in a four-tier system and cases of guiding effect were upgraded of jurisdiction. According to relevant provisions in the Decision of the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress on Authorizing the Supreme People's Court to Organize and Conduct the Pilot Program of the Reform of the Trial Levels and Functional Orientations of Courts Structured in a Four-Tier System and Notice by the Supreme People's Court of Issuing the Implementation Measures for the Pilot Program of the Reform of Improving the Trial Levels and Functional Orientations of Courts Structured in a Four-Tier System, three cases with universal guiding effect on the application of law were removed to the IP Division of Shanghai High People’s Court, including DingTalk Technology Co., Ltd. et al. v. Chengdu Heshi Hongqigong Catering Management Co., Ltd. et al. over trademark infringement and unfair competition dispute, in a bid to advance the pilot program of reform.
(3) The mechanism of Split-flowing complicated cases and simplified ones was promoted to improve the fast-track sentencing mechanism. Yangpu Primary People’s Court vigorously promoted the working method of “Quick trial of Simple Cases, Sophisticated Trial of Complicated Cases, and Special Trial of Similar Cases”, and established a quick trial team dedicated for cases involving e-commerce platforms and the right of making available to the public. The court also formulated the Operational Guideline of the Intellectual Property Division of Yangpu Primary People’s Court for Factor-oriented Trial of Small Claims Procedures, and prepared the flow diagrams, case factors forms, trial outlines and documents in the form of sheets to provide guidance for efficient and quick trial of simple cases.
(4) The diversified dispute resolution mechanism was deepened to promote the governance of litigation source. Shanghai High People’s Court and WIPO Arbitration and Mediation Center signed the Memorandum of Understanding on Strengthening Exchanges and Cooperation on Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) in Intellectual Property Domain to promote the improvement of international diversified IP dispute resolution mechanisms. By the end of 2021, WIPO’s Shanghai Center for Arbitration and Mediation had been entrusted to mediate 41 foreign-related IP cases, among which 14 were settled. Shanghai High People’s Court and Shanghai IP Administration jointly issued the Implementation Measures for Launching the Pilot Program in Shanghai Municipality of Judicial Confirmation Procedures for Administrative Mediation Agreements on Intellectual Property Disputes and Implementation Opinions on Establishing the Litigation and Mediation Linking Mechanism for Civil Intellectual Property Disputes, to coordinate city-wide professional IP mediation efforts and carry out trans-regional civil IP dispute mediation and further improve the diversified dispute resolution mechanism. Putuo Primary People’s Court actively explored the specially-invited mediator mechanism in administrative authorities to set up a trans-regional IP mediation platform. Yangpu Primary People’s Court made a civil ruling confirming the validity of the administrative mediation agreement in a case involving GI certification trademark, which was the first case of judicial confirmation of administrative IP mediation agreement in Shanghai.
(5) Active efforts were made to explore the model of full-process online case handling to resolve disputes online. Since launching the pilot program of full-process online case handling in the end of 2020, Xuhui Primary People’s Court actively explored such factor-oriented mechanism to handle IP cases online, and accepted more than 3,000 IP lawsuits filed by means of factor-oriented filing. The court participated in the formulation of the Working Rules for Full-process Online Handling of Intellectual Property Cases Involving E-commerce Platform and other procedure rules, as well as Guideline for Online Factor-oriented Case Filing and Litigation and “Mobile Micro Court” User Manual (Edition of the Parties); established data interaction channels with e-commerce platforms involved in a relatively large number of IP cases within its jurisdiction to realize online transmission of the data of shops and commodities involved in the cases and pleadings; explored new measures for electronic delivery of non-plaintiff parties; and actively developed new models of litigation. Pudong New Area Primary People’s Court relied on the “Cloud” online trial system of Shanghai High People’s Court and the third-party “Xiaoyu Link” system to continuously promote the application of online mediation and sentencing system, which was recognized by President Zhou Qiang of the Supreme People’s Court of China as “Pudong New Area Primary People’s Court has actively explored a new mode of online settlement of intellectual property disputes, which has achieved remarkable results and is worth summarizing and disseminating.”
(6) Efforts were made to optimize the professional fact finding mechanism. An expert consultation system for IP value evaluation of Shanghai courts was established and the consultation experts were invited to hold the seminar themed with “IP value realization: judicial policies and paths”, in order to provide a more reliable method for determining the amount of damages and promote the matching of damages with the market value of IPRs. The Technical Investigation Office of Shanghai IP Court actively explored inter-court case entrusting mechanism and held panel discussions with trial departments to serve the city-wide fact finding demands in IP case trials.
VI. Law enforcement and case handing ability improved through investigation and research
(1) Guidelines on unifying the application of laws were issued. Shanghai High People’s Court formulated and issued the Work Measures for Strengthening the Uniform Application of Laws in Intellectual Property Cases to build and improve the mechanism of problem finding, conference and application mechanism based on the uniform application of laws and promote the uniform application of laws in similar case trials. The IP Division of Shanghai High People’s Court formulated and issued the Answers to Questions on Calculating the Amount of Damages for Copyright Infringement by Karaoke Operators to reasonably determine the amount of damages and standardize the order to use copyrights in the karaoke industry.
(2) Guidelines on key points in handling cases were developed in detail. The IP Division of Shanghai High People’s Court took the lead in completing the Guidelines on Key Points in Handling Cases of Copyright Disputes, guided Yangpu Primary People’s Court to complete the compilation of the Guidelines on Key Points in Handling Cases of Franchise Contract Disputes and summarized common problems and key points in trials to effectively lead the standardized trial of similar cases. The Criminal Division of Shanghai Third Intermediate People’s Court organized the compilation of the Guidelines on Key Points in Handling Cases of Trademark Infringement Crimes to summarize criminal judicial experience of trademark infringement crimes in a timely manner.
(3) Great efforts were made to carry out model research programs. The IP Division of Shanghai High People’s Court carried out the Research on the Legal Regulations of Providing “Either-or Choice” by An E-commerce Platform, a project initiated by Shanghai Judicial Think Tank, and launched the compilation work of Selected IP Cases of Shanghai Courts. Under the guidance of the IP Division of Shanghai High People’s Court, Pudong New Area Primary People’s Court co-organized with IP Economy the “Forum on the Practical Application of Unfair Competition Principles and Provisions Regarding the Internet”, at which the court issued a research report on the application of special miscellaneous provisions concerning the Internet and model cases over unfair competition on the Internet. The IP Division of Shanghai High People’s Court, Shanghai Intellectual Property Court, Pudong New Area Primary People’s Court and Xuhui Primary People’s Court jointly compiled papers titled Institutional Problems Have Restricted the Promotion of Anti-monopoly Work and Several Platforms Improperly Obtain Data and Carry Out Unfair Competition, and the Protection of Personal Information Needs to be Strengthened, which were published in a bulletin of the Supreme People’s Court and re-posted by the General Office of the CPC Central Committee. The Criminal Division of Shanghai Third Intermediate People’s Court of Shanghai Municipality participated in the compilation of the book titled Judicial Rules for Criminal Intellectual Property Cases in the series of Special Research on Similar Case Retrieving and judging Rules for Chinese Courts, and three judicial rules submitted were selected in this book. Pudong New Area Primary People’s Court compiled the New Features in Unfair Competition Disputes Involving E-Commerce Platforms Requires Attention, which was chosen as an excellent piece of information in 2020 by the General Office of the Supreme People’s Court, and carried out and successfully concluded the Research on the Judicial Protection of Intellectual Property Rights in China’s Cultural and Creative Industries under the Background of Digital Economy, a major project on judicial statistical analysis initiated by the Supreme People’s Court.
(4) Professional trainings were carried out. Menu-type training programs were carried out for IP divisions in Shanghai, a new model of online centralized training was explored, and senior judges of the Supreme People’s Court, experts and scholars of universities and representatives of relevant sectors were invited to give lectures. A special training course on the compensation for IP damages was held, at which Professor Long Xiaoning in economics of Xiamen University was invited to give a lecture on “Economic Analysis in IP Lawsuits: Principles, Methods and Cases”.
2022 marks a key year for implementing the 14th Five-year Plan for China’s national development, and the Communist Party of China will hold its 20th National Congress this year. Shanghai courts will follow the guidance of Xi Jinping Thought on Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era, implement the guiding principles of the Party’s 19th National Congress and all plenary sessions of the 19th Party Central Committee, as well as the central conferences on work related to people’s congresses and the political and legal work, carry forward the great Party-founding spirit, and draw wisdom and strength from the major achievements and historical experience of the Party over the past century. The courts will conscientiously implement the 15-year plan (2021-2035) on the development of IP rights power, strengthen the protection of IP rights in key areas such as e-commerce platforms, digital economy as well as cultural and creative industries, enhance the protection of scientific and technological innovation achievements with greater strength, maintain fair and orderly competition in the market with increased practical measures. The courts will strive to build a professional team that meets the needs of IP judicial development in Shanghai, and continue to improve the law-based business environment, so as to provide better judicial IP services and guarantee for further building Shanghai into a technology innovation hub and accelerating the building of a modern socialist international metropolis with world influence.
-
Previous:
-
Next: